Payload Instrument (Institution) | Measurement Quantity | Innovation |
High Energy Particle Telescope (HEPT; UofA) | Space Radiation: medium energy electrons and solar energetic particles | Unique EPP-related atmospheric energy input, with essential pitch angle resolution |
X-ray Imager (XRI; UofC) | X-rays: emitted from medium energy electrons hitting the atmosphere | Unique imaging of EPP; define area over which precipitation occurs |
Fluxgate Magnetometer (FGM; UofA) | DC magnetic field: Direction and ultra-low frequency plasma waves | Define pitch angle; assess physical role in radiation scattering into the atmosphere |
Search Coil Magnetometer (SCM; UofA) | AC Magnetic Field: Higher frequency plasma waves | Assess physical role in radiation scattering into the atmosphere. |
HEPT will be comprised of 2 sets of 4 detector subassemblies connected to a central electronic box:
- 2 HEPT-HE High Energy Particle Detectors (HE1 & HE2)
- 2 HEPT-LE Low Energy Particle Detectors (LE1 & LE2)
- 2 HEPT-MB-HE Microburst Detectors (MB-HE1 & MB-HE2)
- 2 HEPT-MB-LE Microburst Detectors (MB-LE1 & MB-LE2)
The two sets of subassemblies will be mounted such that the apertures of are pointing in opposite directions (i.e. 180° apart).
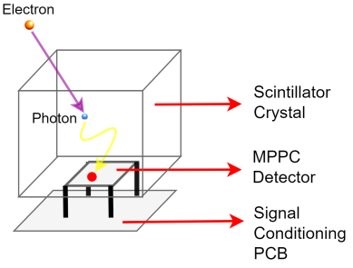
The Microburst detectors are Multi-Pixel Photon Counter (MPPC) / Silicon Photomultiplier (SiPM) based Scintillation detectors designed to identify the occurrence of electron microburst precipitation events in the 0.2 to 3 MeV range. They will be used to trigger changes to sampling rates and data aggregation parameters for the particle telescopes during microburst events.
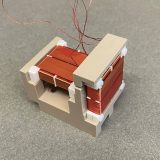
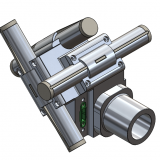
Magnetometer Instrument | Measurement |
Fluxgate FGM | Earth’s B field -> pitch angle |
Search Coil SCM | ELF/VLF waves (~300 Hz – 10 kHz) |
- Energetic electrons that hit the atmosphere generate X-rays as they slow down
- XRI will image these hard X-rays (50-600 keV) to map the spatial distribution and energy spectrum of precipitating particles
- 2 imagers on opposite sides of the SC
- Field of View (FOV): 90° x 90° each
- As the spacecraft spins, the FOV sweeps across the ground track underneath
- Electron detectors mounted on top complement the HEPT suite detectors by measuring electron spectrum in the 50-300 keV range
XRI: A-side
- Based on AXIS imager on the AEPEX CubeSat mission
- Solid-state detectors, coded aperture imaging
- Good spatial resolution
- Moderate background rejection
- Limited energy range
XRI: B-side
- Simple design
- Collimated scintillators
- Very good background rejection
- Good energy range
- Moderate spatial resolution